Category: Uncategorised
Nutritional Management During Fasting Month of Ramadan
05 April 2023 | Article is written by Mohammad Noor Hisham (Dietitian, Lovy Pharmacy)
This article is reviewed by dietitian Tan Jun Er and nutritionist Yeu Yi Wen (Lovy Pharmacy)
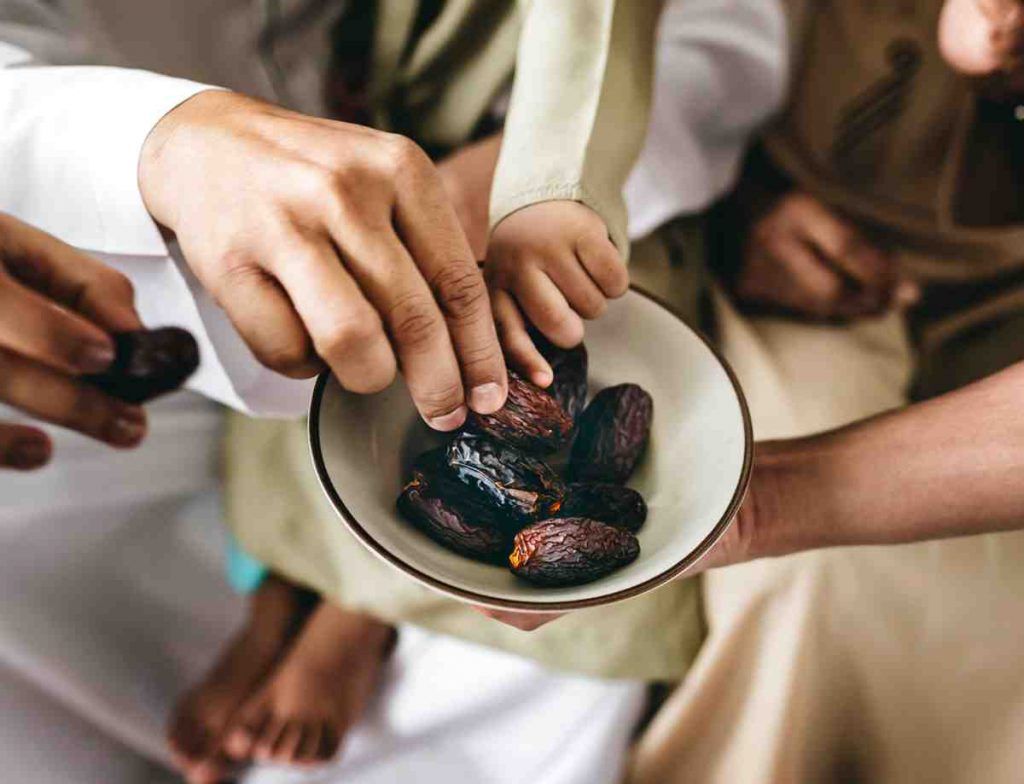

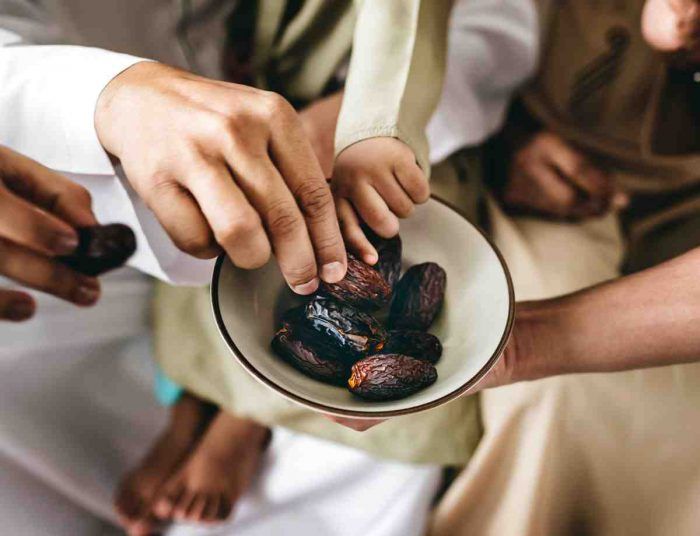
(Image credit: Freepik)
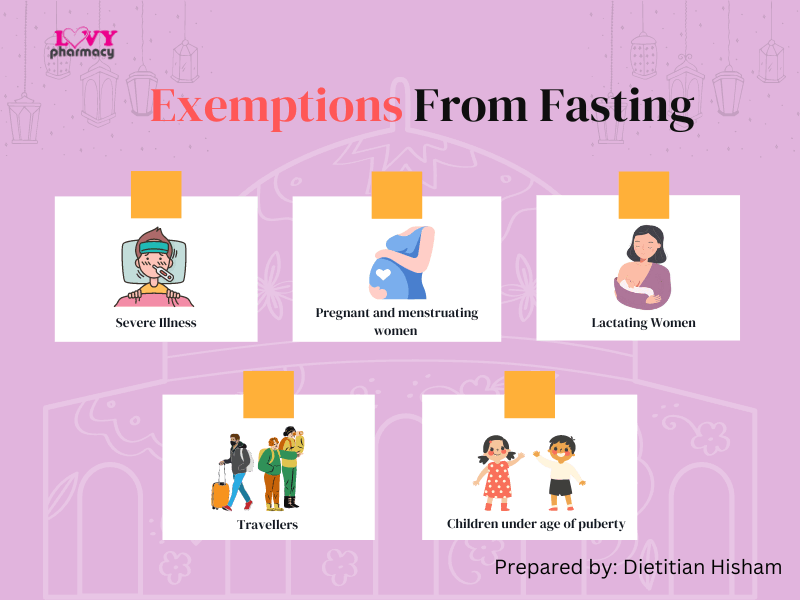
Muslims around the world are nearly halfway through the holy month of Ramadan, during which Muslim adults and adolescents who have reached puberty abstain from eating and drinking from dawn to dusk. In Southeast Asian countries like Malaysia, the average fasting hours range from 12 to 14 hours a day. Certain groups such as pregnant and lactating women, and individuals with severe illnesses, are exempted from fasting for health reasons.
As we approach the final 15 days of Ramadan, it is important to maintain proper nutrition intake. In this post, we will look into eating habits to avoid, nutritional management for diabetic patients, and Ramadan nutrition meal plans.
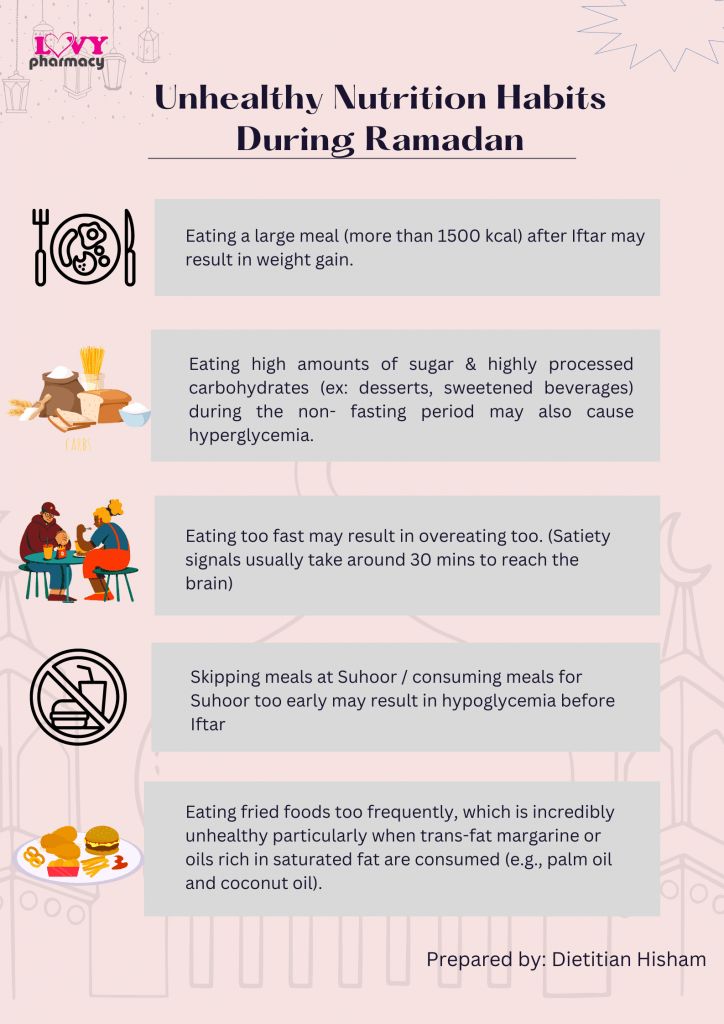
Eating Habits to Avoid During Ramadan
Though it is known that fasting during Ramadan has its list of health benefits, following most of our cravings during iftar and not having a balanced meal during suhoor can lead to a harmful eating pattern that might cause health problems.
Nutritional Management for Diabetic Patients
Fasting during Ramadan for people with diabetes carries considerable challenges. Despite that, many diabetic patients still insist on fasting. Healthcare professionals (HCPs) must be conscious of the potential dangers of fasting for some individuals with diabetes and should quantify and stratify the risks for every individual to provide the best possible care. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, discuss with your doctor and dietitian before fasting during Ramadan.
Consult our doctors and dietitians via Live Chat feature within our Doctor2U app.
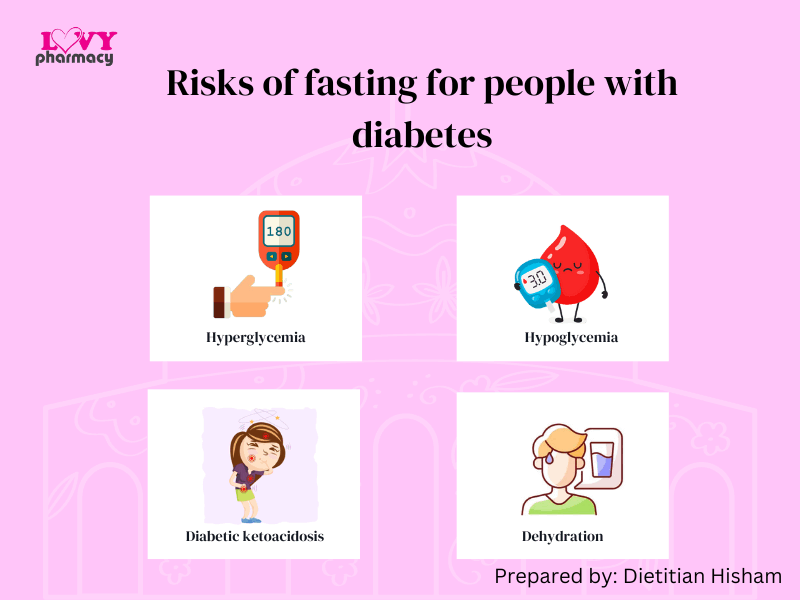

Ramadan Nutrition Plan (RNP) for Diabetes Patients
Ramadan Nutrition Plan (RNP) is a clinically proven tool, designed to assist individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) to achieve better blood glucose control and help with weight management. This plan can also be applied for the general population.
The “Ramadan plate” method may be used for designing meals.
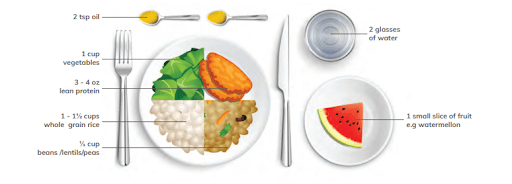
(Image credit: IDF-DAR Practical Guideline 2021)
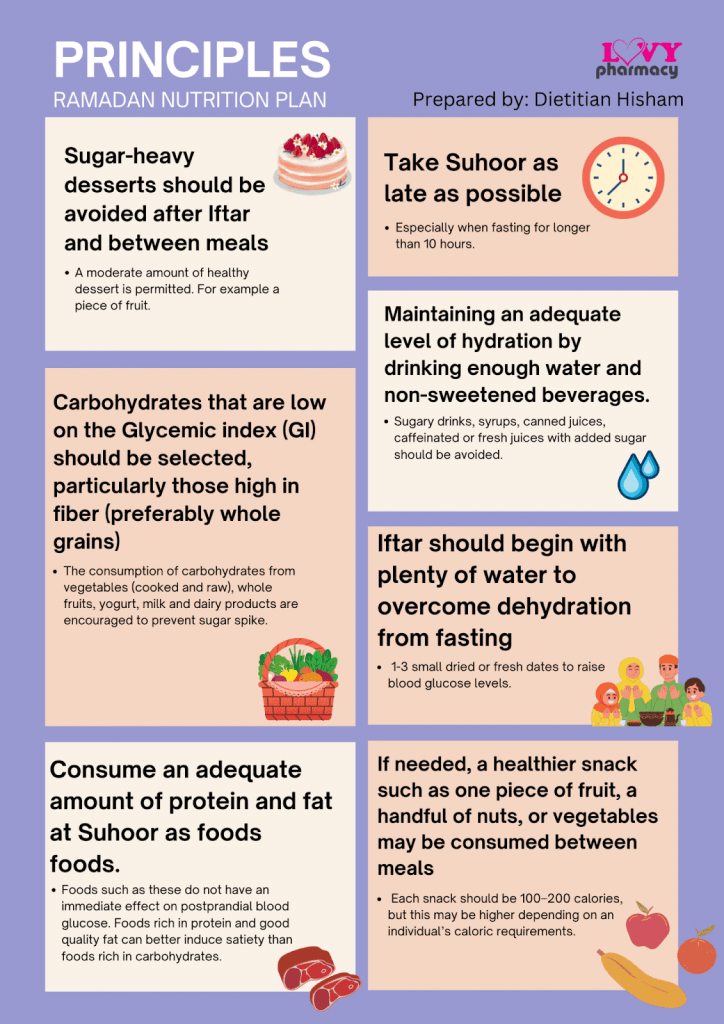
Glycemic Index (GI): A measure of the increase in the level of blood sugar caused by eating a specific carbohydrate.
Managing Digestive Issues During Fasting
The reduction in food intake that comes along with fasting may cause digestive issues such as constipation, diarrhoea, nausea, and bloating. It is best to support your fasting journey and enhance the benefits of fasting with probiotic supplementation that contains Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains.
Our Nutridos Bifido mixed berries juice powder is rich with probiotics to help improve good gut bacteria. The juice powder is free from sugar, colourant and artificial flavouring, making it a healthier choice of drink

Purchase Nutridos Bifido mixed berries juice to enjoy its nutritional benefits.
Here is a sample of nutritious and tasty meal plans during the fasting month:
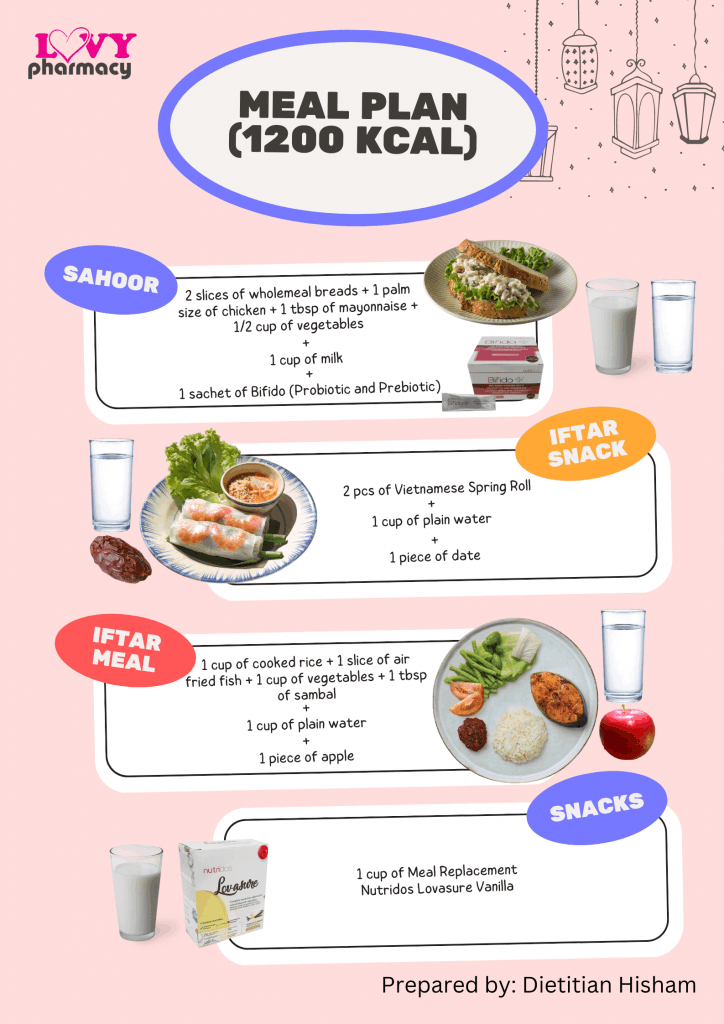
In short, practising mindful eating during Ramadan can help with blood sugar control as well as weight management. Remember to avoid excessive refined carbohydrate intake, choose low Glycemic Index (GI) carbohydrates, and consume plenty of water. We hope you have a smooth journey in the remaining days of this fasting month. Selamat berpuasa!
References
- Bashier, A.M., et al., Impact of optimum diabetes care on the safety of fasting in Ramadan in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on insulin therapy. Diabetes research and clinical practice, 2019. 150: p. 301-307.
- El Toony, L.F., D.A. Hamad, and O.M. Omar, Outcome of focused pre-Ramadan education on metabolic and glycaemic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 2018. 12(5): p. 761-767.
- Hamdy, O., et al., The Ramadan Nutrition Plan (RNP) for Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes and Ramadan: practical guidelines [Internet], 2017: p. 73-83.
- Hassanein M;Afandi B;Yakoob Ahmedani M;Mohammad Alamoudi R;Alawadi F;Bajaj HS;Basit A;Bennakhi A;El Sayed AA;Hamdy O;Hanif W;Jabbar A;Kleinebreil L;Lessan N;Shaltout I;Mohamad Wan Bebakar W;Abdelgadir E;Abdo S;Al Ozairi E;Al Saleh Y;Alarouj M;Ali T;Ali Al. (2021.). Diabetes and ramadan: Practical guidelines 2021. Diabetes research and clinical practice. Retrieved March 15, 2023, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35016991/.
- Tourkmani, A.M., et al., Impact of Ramadan focused education program on hypoglycemic risk and metabolic control for patients with type 2 diabetes. Patient preference and adherence, 2016. 10: p. 1709.
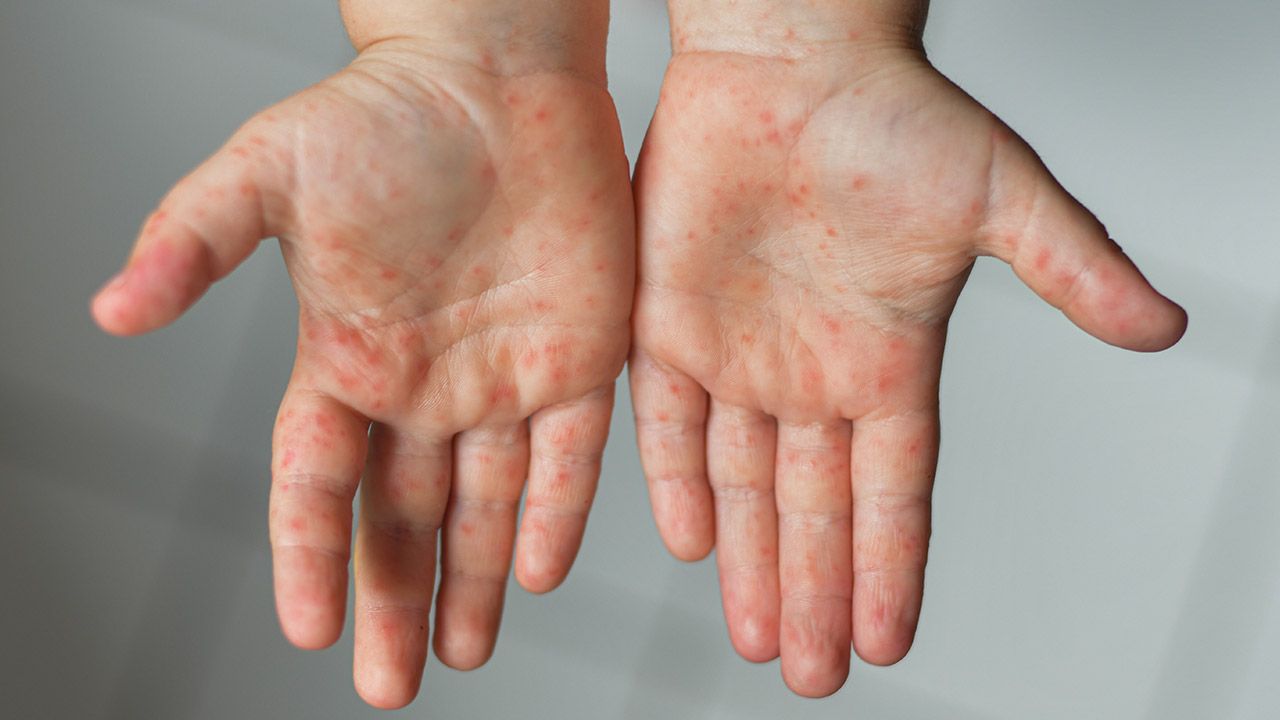
Hand, Foot & Mouth Disease (HFMD)
[vc_row][vc_column]

Overview
HFMD is a viral infection caused by a group of enteroviruses, most commonly the Coxsackie virus. The incubation period of HFMD is 3 to 5 days (with a range from 2 days to 2 weeks). Both adults and children can be affected, but young children below 5 years old are more susceptible.[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Signs and Symptoms
- Fever.
- Lethargy.
- Poor appetite.
- Sore throat.
- Mouth ulcers on the inside of the mouth or sides of the tongue.
- Rash (flat or raised spots) or small blisters on palms of hands, soles of feet, and/or buttocks.
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
How does it spread?
HFMD spreads through direct contact with:
- Nasal discharge.
- Saliva.
- Faeces and fluids from the rash of an infected person.
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Is there any treatment?
Currently there is no specific effective treatment except for symptoms relief methods.[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
If your child has HFMD, please take the following actions:
- Inform school, nursery, kindergarten, so that they can monitor other children closely and prevent further spread of HFMD.
- Keep your child away from public.
- Check other family members whether they have any signs and symptoms of HFMD.
- Proper disinfection of appliances or toys that are contaminated.
- Avoid sharing food and utensils.
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
4 CHECKS whether your child is fit for school:
- Check for fever (to take temperature).
- Check for blisters on hands and arms.
- Check for mouth ulcers.
- Check for blisters on soles of feet, legs and/or buttocks.
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
For more info
Please refer to the following website:
[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”4176″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][vc_empty_space height=”10vh”][/vc_column][/vc_row]